How to count lines of source code in Linux
Last updated on May 31, 2020 by Dan Nanni
For various reasons you may want to know in how many lines of code given open-source software is implemented. For example, you want to estimate the effort devoted to developing a particular open-source program. Or you want to gauge the size and complexity of a program before trying it. There is some controversy as to using source lines of code (SLOC) as a metric to determine the size of a software program, since existing programming languages differ greatly in terms of clarify and brevity.
In any rate, if you would like to count the number of source code lines quickly and accurately, you can use a command-line tool called cloc (short for "Count Lines Of Code"). cloc is a Perl program that is dedicated to counting the number of lines of code. To estimate the size of codebase accurately, cloc automatically detects different types of programming/scripting languages, and discounts comment lines and blank lines based on the type appropriately.
Install cloc on Linux
For Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint:
$ sudo apt install cloc
For CentOS or RHEL:
To install cloc on CentOS/RHEL, first enable EPEL repository and then run:
$ sudo yum install cloc
For Fedora:
cloc is available in the base repository, so simply run:
$ sudo dnf install cloc
Check the Number of Lines of Code with cloc
The basic usage of cloc is as follows.
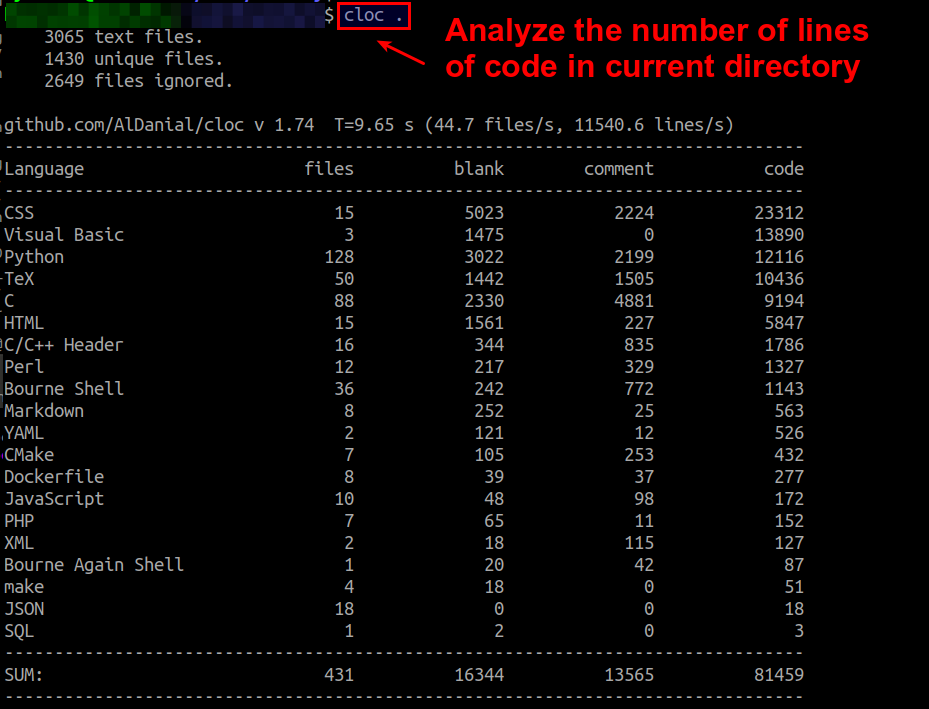
$ cloc .
cloc will then look for source code files in the current directory and all its sub-directories recursively, detects the type of language used in each file, and counts the number of lines of code. As shown below, the final summary shows the breakdown of number of lines of code for different programming languages.
If you want to count the total number of lines of code in a particular set of files (e.g., *.py), you can run the following command.
$ find . -name "*.py" | xargs cloc
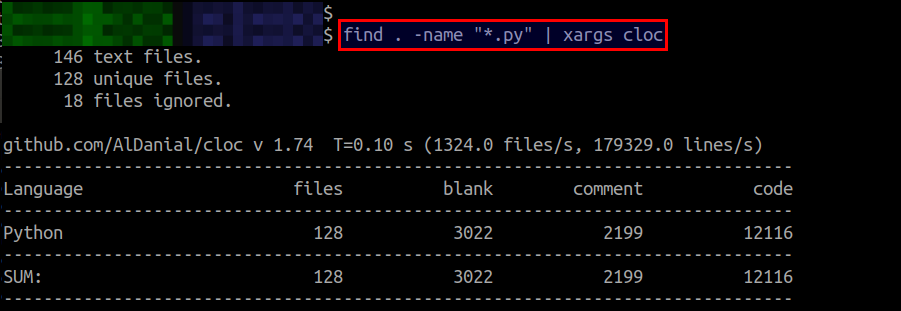
In the above example, we consider only Python source code and count the number of lines of Python code.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

