How to set up EPEL repository on CentOS
Last updated on January 17, 2021 by Dan Nanni
If you are using CentOS or RHEL, it is often recommended that you configure EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) repository on your system. EPEL is a community effort to create a repository of high-quality close to 7,000 add-on software packages for RHEL-based distributions. Once you set up EPEL repository, you can use yum command to install any of those EPEL packages.
In order to enable EPEL repository on your CentOS system, you need to check your CentOS version as follows.
$ cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 8.3.2011
Then install a corresponding EPEL release RPM package as described in this tutorial. Note that the EPEL release RPM does not depend on the underlying processor architecture (e.g., 32-bit/64-bit x86, ppc, sparc, alpha, etc), so no need to pay attention to processor architecture difference.
Set up EPEL Repository on CentOS 8
CentOS 8 includes an RPM package for EPEL repositoryn in its base repository. So simply use yum to enable EPEL repository.
$ sudo yum install epel-release
Note that some EPEL packages may rely on packages from PowerTools repository. Thus it is recommended that you also enable PowerTools along with EPEL on CentOS 8.
Set up EPEL Repository on CentOS 7
Starting from CentOS 7, EPEL release RPM package is available in extras repo. Therefore, simply use yum command to set up EPEL repository on CentOS 7 platform:
$ sudo yum install epel-release
Set up EPEL Repository on CentOS 6 or Earlier
For earlier versions of CentOS, you can use rpm command to download and install an RPM file manually as follows.
For CentOS/RHEL 6.*:
$ sudo yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-6.noarch.rpm
Note that CentOS/RHEL 5 or earlier has already reached End-of-Life, and are not supported.
Import EPEL Repository's GPG Key
During installation, you may see the following warning, which indicates that EPEL's GPG key is missing.
warning: /var/tmp/rpm-tmp.3TKM2G: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID 0608b895: NOKEY
The EPEL's official GPG key is found in /etc/pki/rpm-gpg. Thus go ahead and import the GPG key as follows.
For CentOS/RHEL 8:
$ sudo sudo rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-8
For CentOS/RHEL 7:
$ sudo sudo rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
For CentOS/RHEL 6.*:
$ sudo sudo rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-6
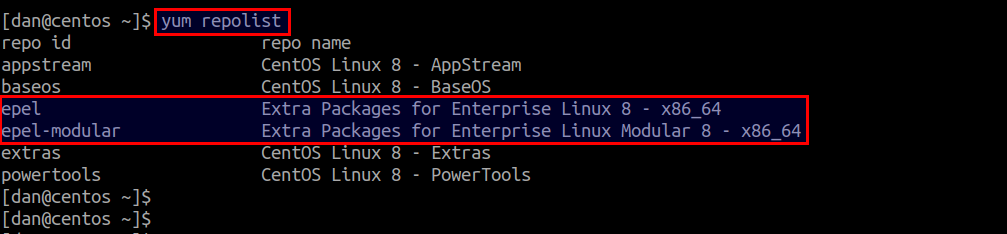
To verify that EPEL repository has been set up successfully, run the following command to list all available repositories on your system.
$ yum repolist
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

