How to monitor a Linux server and desktop remotely from web browser
Last updated on September 21, 2020 by Dan Nanni
When it comes to monitoring a Linux box, there are more than enough options to choose from. While there are many production-quality monitoring solutions (e.g., Nagios, Zabbix, Zenoss), boasting of fancy UI, monitoring scalability, comprehensive reporting capabilities, etc., these solutions are probably an overkill for most of us end users. If all you need is to check the basic status (e.g., CPU load, memory usage, active processes, disk usage) of a remote Linux server or desktop, consider linux-dash.
linux-dash is a web-based lightweight monitoring dashboard for Linux machines, which can display, in real-time, various system properties, such as CPU load, RAM usage, disk usage, Internet speed, network connections, RX/TX bandwidth, logged-in users, running processes etc. linux-dash does not come with any backend database for storing long-term statistics. Simply drop in linux-dash app in an existing web server (e.g., Apache, Nginx), and you are good to go. It is a quick and easy way to set up remote monitoring for personal projects.
In this tutorial, I am going to describe how to set up linux-dash in Nginx web server on Linux. Nginx is preferred over Apache web server due to its lightweight engine.
Set up linux-dash on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint
First, install Nginx web server with php-fpm.
$ sudo apt-get install git nginx php5-json php5-fpm php5-curl
Configure Nginx for linux-dash app by creating /etc/nginx/conf.d/linuxdash.conf as follows. In this example, we are going to use port 8080.
$ sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/linuxdash.conf
server {
server_name $domain_name;
listen 8080;
root /var/www;
index index.html index.php;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location ~* .(?:xml|ogg|mp3|mp4|ogv|svg|svgz|eot|otf|woff|ttf|css|js|jpg|jpeg|gif|png|ico)$ {
try_files $uri =404;
expires max;
access_log off;
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
}
location /linux-dash {
index index.html index.php;
}
# PHP-FPM via sockets
location ~ .php(/|$) {
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock;
if (!-f $document_root$fastcgi_script_name) {
return 404;
}
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Disable the default site configuration.
$ sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Configure php-fpm by editing /etc/php5/fpm/pool.d/www.conf. Make sure to edit user, group and listen directives as shown below. You can keep the rest of the configuration unchanged.
$ sudo vi /etc/php5/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
. . . user = www-data group = www-data listen = /var/run/php5-fpm.sock . . .
Proceed to download and install linux-dash.
$ git clone https://github.com/afaqurk/linux-dash.git $ sudo cp -r linux-dash/ /var/www/ $ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www
Restart Nginx web server as well as php5-fpm to finalize installation.
$ sudo service php5-fpm restart $ sudo service nginx restart
Set up linux-dash on CentOS, Fedora or RHEL
On CentOS, it is necessary to enable EPEL repository first.
Install Nginx web server and php-fpm component.
$ sudo yum install git nginx php-common php-fpm
To configure Nginx for linux-dash app, create /etc/nginx/conf.d/linuxdash.conf as follows.
$ sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/linuxdash.conf
server {
server_name $domain_name;
listen 8080;
root /var/www;
index index.html index.php;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location ~* .(?:xml|ogg|mp3|mp4|ogv|svg|svgz|eot|otf|woff|ttf|css|js|jpg|jpeg|gif|png|ico)$ {
try_files $uri =404;
expires max;
access_log off;
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
}
location /linux-dash {
index index.html index.php;
}
# PHP-FPM via sockets
location ~ .php(/|$) {
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?.php)(/.*)$;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm.sock;
if (!-f $document_root$fastcgi_script_name) {
return 404;
}
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Next, configure php-fpm by editing /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf. In this file, make sure to set listen, user and group fields as below. You can leave the rest of the configuration unchanged.
$ sudo vi /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
. . . listen = /var/run/php-fpm.sock user = nginx group = nginx . . .
Download and install linux-dash under /var/www.
$ git clone https://github.com/afaqurk/linux-dash.git $ sudo cp -r linux-dash/ /var/www/ $ sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www
Finally, restart Nginx web server as well as php-fpm, and set them to auto-start upon boot.
$ sudo service php-fpm restart $ sudo service nginx restart $ sudo chkconfig nginx on $ sudo chkconfig php-fpm on
In this example, we have configured linux-dash to use TCP port 8080. So make sure that the firewall is not blocking TCP port 8080.
Monitor a Linux Machine with linux-dash
To access linux-dash from a web browser, simply go to http://<linux-IP-address>:8080/linux-dash/ on your web browser.
Below are the screenshots of linux-dash. The web dashboard consists of several widgets, each of which displays particular system properties. You can customize the look of the web dashboard by rearranging and/or closing some of the widgets. Check out some of the screenshots of linux-dash.
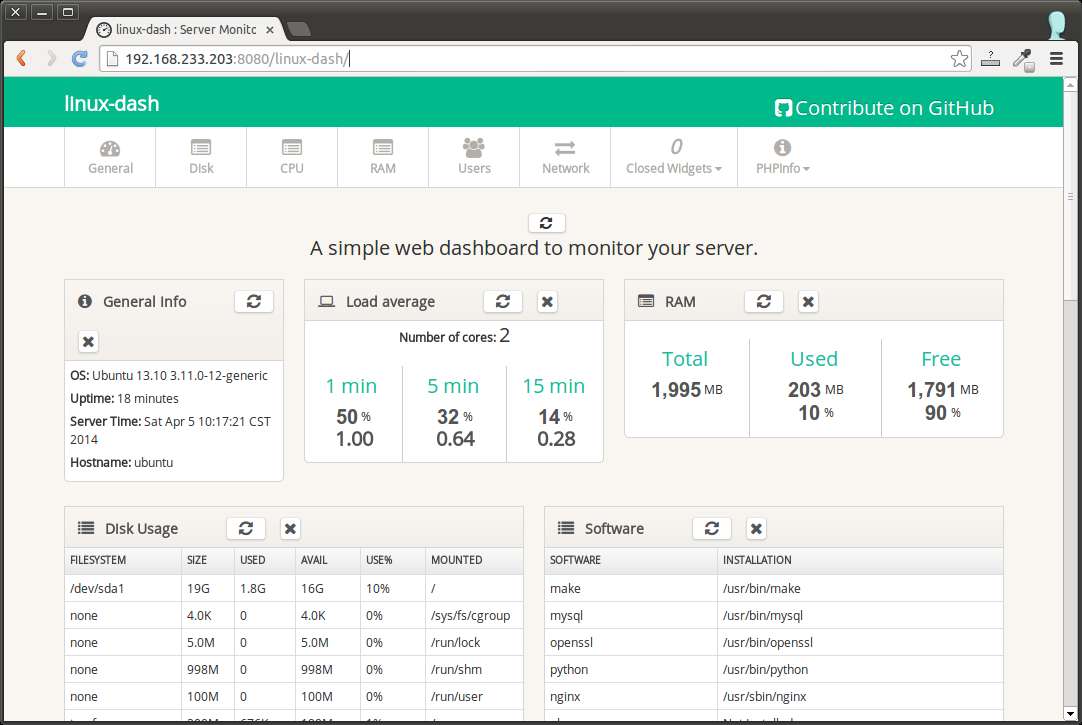

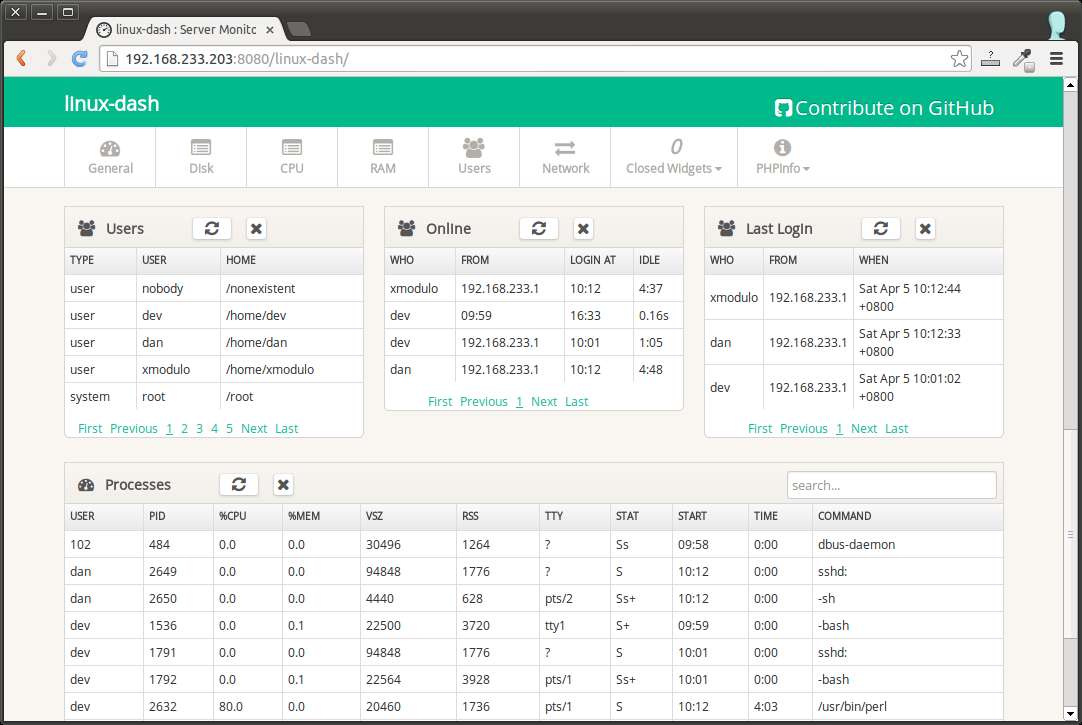
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

