How to check package dependencies on Ubuntu or Debian
Last updated on September 15, 2020 by Dan Nanni
A typical .deb package relies on other packages to install and operate properly. With package managers such as apt-get and aptitude, you can resolve package dependencies, and have all prerequisites installed automatically. Tools like gdebi allows you to detect any dependencies in a .deb file and install all dependent packages along with the .deb file.
Suppose for whatever reason, you want to manually resolve package dependencies of a particular package, in which case you need to identify all its dependent packages first.
In the following, I will explain how to check package dependencies on Ubuntu or Debian.
Check Deb Package Dependencies with apt-rdepends
A command-line tool called apt-rdepends can help you in this case. This tool can recursively check dependencies of .deb package, and list all found package dependencies.
To install apt-rdepends on Ubuntu or Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install apt-rdepends
To show package dependency information of a particular package (e.g., tcpdump), run the command with package name:
$ apt-rdepends tcpdump
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done tcpdump Depends: libc6 (>= 2.14) Depends: libpcap0.8 (>= 1.2.1) Depends: libssl1.0.0 (>= 1.0.0) libc6 Depends: libc-bin (= 2.15-0ubuntu20) Depends: libgcc1 Depends: tzdata libc-bin libgcc1 Depends: gcc-4.7-base (= 4.7.2-2ubuntu1) Depends: libc6 (>= 2.14) PreDepends: multiarch-support . . . .
Visualization of Package Dependencies
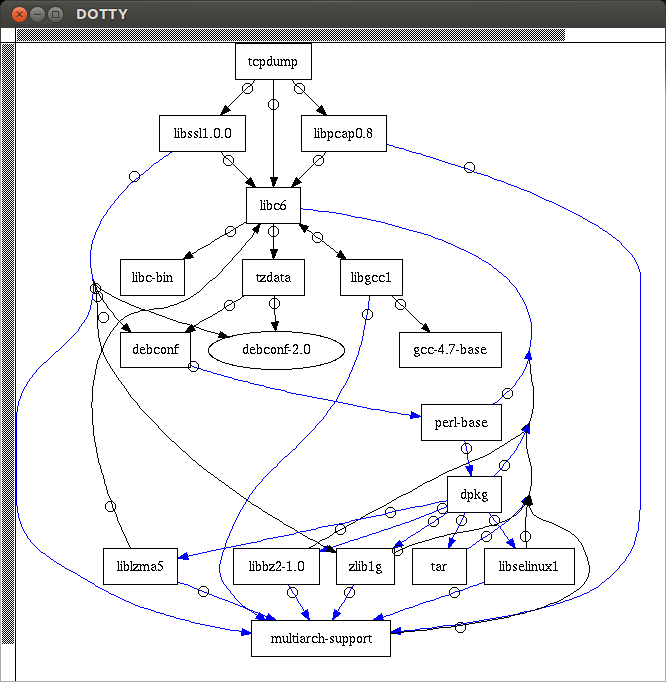
The text output of apt-rdepends can be difficult to read due to many recursively defined dependency relationships. That is when visualization can help. apt-rdepends can export package dependency information into a dot file, which can be used by a GUI-based graph editor called dotty to visualize package dependencies in a graph format.
For visualization, first install dotty graph editor tool:
$ sudo apt-get install graphviz
Finally, run the following commands to visualize package dependencies with dotty:
$ apt-rdepends -d tcpdump | dot > tcpdump.dot $ dotty tcpdump.dot
The visualization result of tcpdump package looks like the following.
So far in this tutorial, we check package dependencies on Debian-based systems. If you want to know more about package dependencies on RPM-based systems such as Fedora or CentOS, please refer to this tutorial.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

