How to set up a Replica Set on MongoDB
Last updated on October 16, 2020 by Dan Nanni
MongoDB has become one of the most famous NoSQL databases on the market. MongoDB is document-oriented, and its scheme-free design makes it a really attractive solution for all kinds of web applications. One of the features that I like the most is Replica Set, where multiple copies of the same data set are maintained by a group of mongod nodes for redundancy and high availability.
This tutorial describes how to configure a Replica Set on MongoDB.
The most common configuration for a Replica Set involves one primary and multiple secondary nodes. The replication will then be initiated from the primary toward the secondaries. Replica Sets can not only provide database protection against unexpected hardware failure and service downtime, but also improve read throughput of database clients as they can be configured to read from different nodes.
Set up the Environment
In this tutorial, we are going to set up a Replica Set with one primary and two secondary nodes.
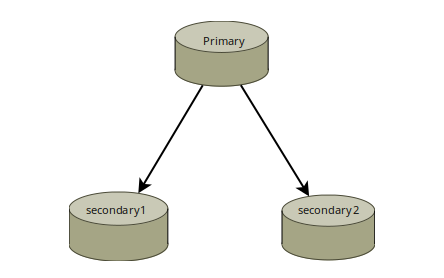
In order to implement this lab, we will use three virtual machines (VMs) running on VirtualBox. I am going to install Ubuntu 14.04 on the VMs, and install official packages for Mongodb.
I am going to set up a necessary environment on one VM instance, and then clone it to the other two VM instances. Thus pick one VM named master, and perform the following installations.
First, we need to add the MongoDB key for apt:
$ sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10
Then we need to add the official MongoDB repository to our source.list:
$ sudo su # echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu "$(lsb_release -sc)"/mongodb-org/3.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
Let's update repositories and install MongoDB.
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
Now let's make some changes in /etc/mongodb.conf.
auth = true dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb logpath=/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log logappend=true keyFile=/var/lib/mongodb/keyFile replSet=myReplica
The first line is to make sure that we are going to have authentication on our database. keyFile is to set up a keyfile that is going to be used by MongoDB to replicate between nodes. replSet sets up the name of our replica set.
Now we are going to create our keyfile, so that it can be in all our instances.
We are going to use md5sum, but we need to clean up an MD5 string before using it in MongoDB. Use the following command to clean it up:
$ echo -n "MyReplicaSetKey" | md5sum|grep -o "[0-9a-z]+" > keyFile
What grep command does is to print MD5 string with no spaces or other characters that we don't want.
Now we are going to make the keyfile ready for use:
$ sudo cp keyFile /var/lib/mongodb $ sudo chown mongodb:nogroup keyFile $ sudo chmod 400 keyFile
Now we have our Ubuntu VM ready to be cloned. Power it off, and clone it to the other VMs.
I name the cloned VMs secondary1 and secondary2. Make sure to reinitialize the MAC address of cloned VMs and clone full disks.
All three VM instances should be on the same network to communicate with each other. For this, we are going to attach all three VMs to Internet Network.
It is recommended that each VM instances be assigned a static IP address, as opposed to DHCP IP address, so that the VMs will not lose connectivity among themselves when a DHCP server assigns different IP addresses to them.
Let's edit /etc/networks/interfaces of each VM as follows.
On primary:
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.50.2
netmask 255.255.255.0
On secondary1:
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.50.3
netmask 255.255.255.0
On secondary2:
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 192.168.50.4
netmask 255.255.255.0
Another file that needs to be set up is /etc/hosts, because we don't have DNS. We need to set the hostnames in /etc/hosts.
On primary:
127.0.0.1 localhost primary 192.168.50.2 primary 192.168.50.3 secondary1 192.168.50.4 secondary2
On secondary1:
127.0.0.1 localhost secondary1 192.168.50.2 primary 192.168.50.3 secondary1 192.168.50.4 secondary2
On secondary2:
127.0.0.1 localhost secondary2 192.168.50.2 primary 192.168.50.3 secondary1 192.168.50.4 secondary2
Check connectivity among themselves by using ping command:
$ ping primary $ ping secondary1 $ ping secondary2
Set up a Replica Set
After verifying connectivity among VMs, we can go ahead and create the admin user so that we can start working on the Replica Set.
On primary node, open /etc/mongodb.conf, and comment out two lines that start with auth and replSet:
dbpath=/var/lib/mongodb logpath=/var/log/mongodb/mongod.log logappend=true #auth = true keyFile=/var/lib/mongodb/keyFile #replSet=myReplica
The auth line needs to be commented out before you configure any user or Replica Sets in new MongoDB installation. By default, MongoDB does not have any user created. Thus if auth is enabled before you create an user, you won't be able to do anything. You can enable auth back after creating a user.
After modifying /etc/mongodb.conf, restart mongod daemon.
$ sudo service mongod restart
Now connect to the MongoDB master from the shell:
$ mongo <master-ip-address>:27017
Once you are in, create an admin user.
> use admin
> db.createUser({
user:"admin",
pwd:"
})
Restart MongoDB.
$ sudo service mongod restart
Connect to MongoDB again, and use these commands to add secondary1 and secondary2 to our Replicat Set.
> use admin
> db.auth("admin","myreallyhardpassword")
> rs.initiate()
> rs.add ("secondary1:27017")
> rs.add("secondary2:27017")
Now that we have our Replica Set, we can start working on our project. Consult the official driver documentation to see how to connect to a Replica Set. In case you want to query from shell, you have to connect to primary instance to insert or query the database. Secondary nodes will not let you do that. If you attempt to access the database on a secondary node, you will get this error message:
myReplica:SECONDARY>
myReplica:SECONDARY> show databases
2015-05-10T03:09:24.131+0000 E QUERY Error: listDatabases failed:{ "note" : "from execCommand", "ok" : 0, "errmsg" : "not master" }
at Error ()
at Mongo.getDBs (src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:47:15)
at shellHelper.show (src/mongo/shell/utils.js:630:33)
at shellHelper (src/mongo/shell/utils.js:524:36)
at (shellhelp2):1:1 at src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:47
If you want to connect to the whole Replica Set from the shell, you can do it as follows. Failover within the Replica Set should be automatic.
$ mongo primary,secondary1,secondary2:27017/?replicaSet=myReplica
If you use other driver languages (e.g., JavaScript, Ruby, etc), the syntax may be different.
I hope you find this tutorial useful. You can use Vagrant to automate your local environments and help you code faster.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

