What are good web server benchmarking tools for Linux
Last updated on December 13, 2020 by Dan Nanni
As far as web server performance is concerned, there are many different factors at play, e.g., front-end application design, network latency/bandwidth, web server configuration, server-side in-memory cache, raw hardware capability, server load of shared hosting, etc. To compare and optimize web server performance under such a wide array of factors, we often perform load test (or stress test) using a web server micro-benchmark tool. A typical benchmark tool injects synthetic workloads or replays real-world traces to a web server, and measures web server performance and scalability in terms of varying metrics (e.g., response time, throughput, number of requests per second, CPU load, etc).
For those of you who want to find out how your web server or web service will measure up under different workload conditions, here are a list of web server benchmark tools available on Linux platforms.
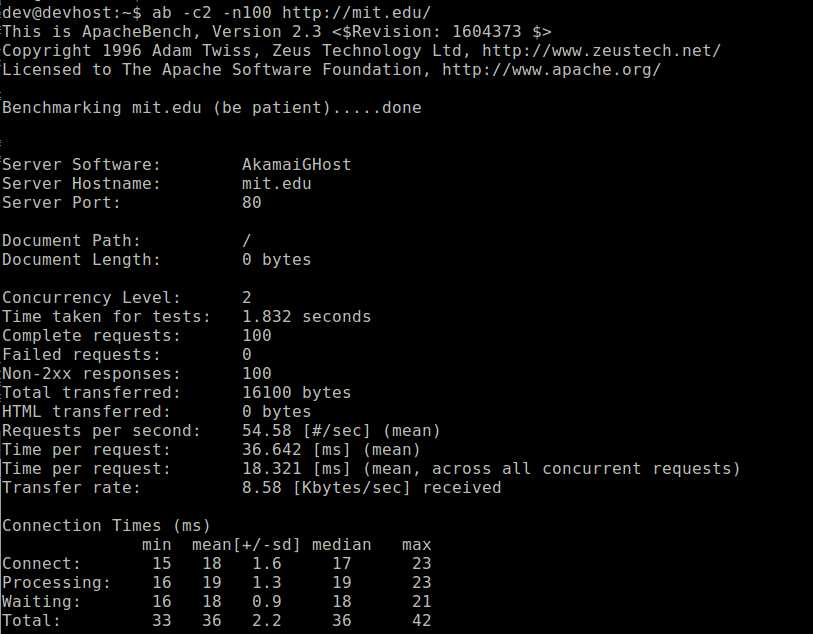
1. ApacheBench
ApacheBench (ab) is a standard command-line web server benchmark tool bundled with Apache HTTP server. It can send an arbitrary list of (concurrent) web requests. Support for POST/PUT/GET requests, as well as basic password authentication is available. Testing results include requests per second, time per request, transfer rate, connection time statistics (min, max, median, mean), etc. License: Apache v2.0.
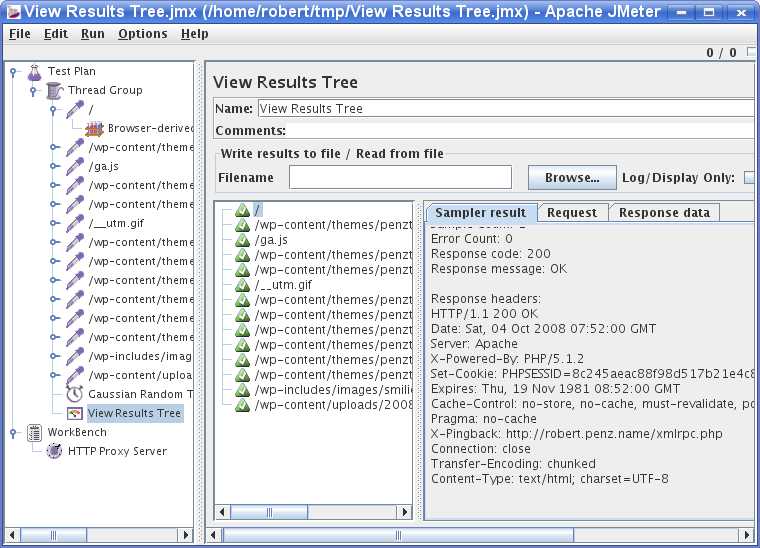
2. Apache JMeter
Apache JMeter is a cross-platform Java-based GUI program designed to stress test any web application. It can be used to test the performance of web-server backends powered by server-side languages (e.g., PHP, Java, ASP.NET) or databases (e.g., JDBC, LDAP, MongoDB). It provides highly pluggable testing architecture via extensible data visualization GUI. License: Apache v2.0.
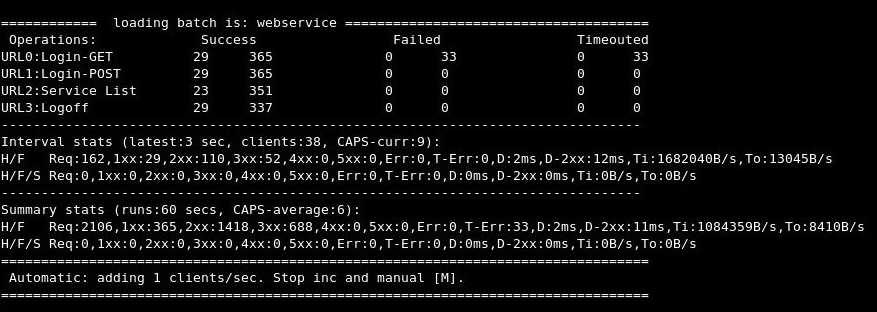
3. curl-loader
curl-loader is a command-line application workload generator which can simulate multiple HTTP/HTTPS FTP/FTPS clients. Simulated clients can conduct various tasks, such as authenticated login (POST or GET/POST), GET/POST/PUT requests from batch configuration with probabilistic distribution, FTP passive/active operations, HTTP logoff (POST, GET/POST, GET with cookie), etc. Per-client status and statistics are logged to a file. License: GPLv2.
4. FunkLoad
FunkLoad is a web server load testing tool written Python. It can perform functional unit testing, as well as stress and longevity testing. Features include GET/POST/PUT/DELETE requests, basic authentication, cookie, HTTPS with SSL/TLS, browser cache emulation, and CSS/image/JavaScript fetching. License: GNU GPL.
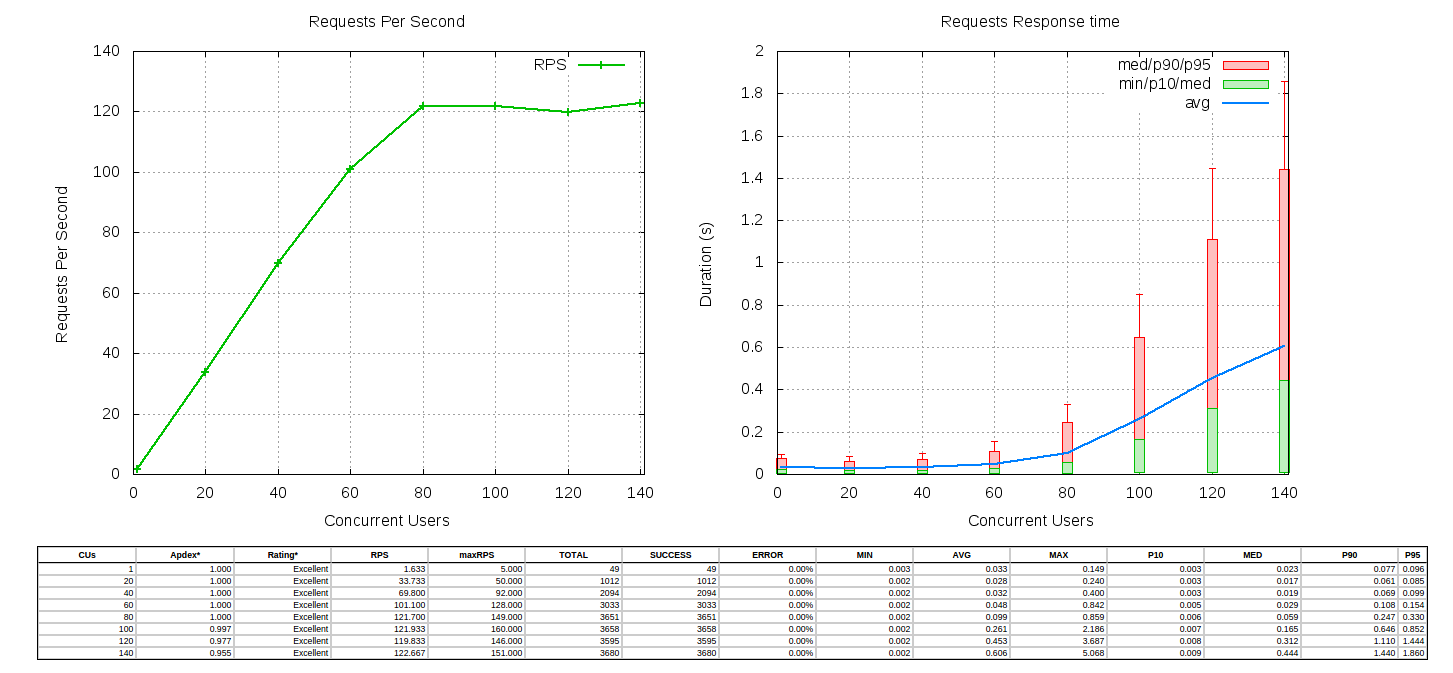
5. Gatling
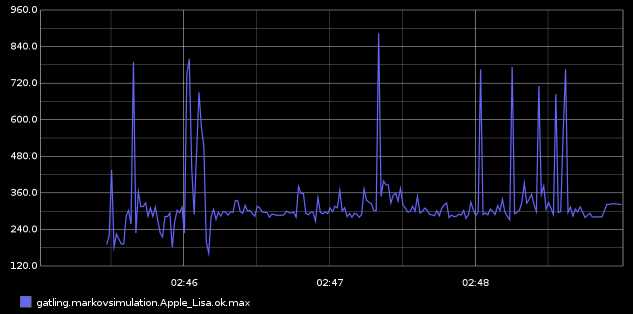
Gatling is an open-source protocol-agnostic load testing tool primarily used to benchmark HTTP servers and web services. Using a lightweight asynchronous testing engine, it can easily simulate thousands of concurrent users whose web browsing behaviors and scenarios (e.g., login, browse product listings, add a product to cart, check out) are independently scripted. It supports real-time reports via the Graphite protocol, and can be integrated via extensions with other third-party building tools such as Maven, Jenkins, SBT. License: Apache v2.0.
6. Httperf
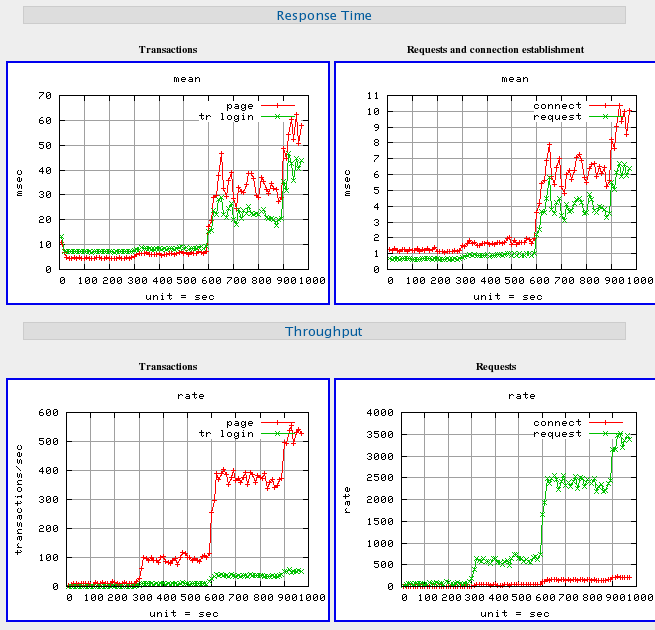
Httperf is an HTTP workload generator command-line tool which can generate a number of different types of HTTP traffic, including GET/HEAD/PUT/POST requests, HTTP pipelining, SSL traffic, stateful sessions with cookie, etc. Output includes connection rate, connection time statistics (min, max, median, stddev), request/reply rate, and network throughput. License: GNU GPLv2.

7. Pylot
Pylot is a Python-based performance and scalability testing tool for web services. It generates multi-agent workload scenarios based on test cases defined in an XML file, and displays stats and error reporting results in real-time. It supports HTTPS/SSL, cookie handling, regular expression based response verification, multi-threading, console/GUI modes. License: GNU GPLv3.

8. Siege
Siege is an HTTP load testing and benchmarking tool for terminal environment. Support for basic password authentication, cookies, HTTPS with SSL is available. License: GNU GPL.
9. The Grinder
The Grinder is a Java-based multi-threaded test framework which can perform load test and functional test of various application and network protocols written in Java APIs, including as HTTP servers, SOAP, XML-RPC, REST web services, JMS, JDBC, RMI, and POP3/SMTP/LDAP. It supports dynamic loading and monitoring of test scripts written in Jython and Clojure languages, and allows injecting load from multiple machines in the distributed fashion. Its HTTP support includes cookie handling, SSL, connection rate-limiting, trace record and replay, proxy, etc.
10. Tsung
Tsung is an open-source multi-protocol stress test tool which can generate different types of workloads for HTTP, SSL, WebDAV, SOAP, PostgresSQL, MySQL, LDAP, XMPP servers. With HTTP server testing, it supports basic requests (GET/POST/PUT/DELETE/HEAD), cookies, authentication with password or oAuth, SOAP, graph visualization and HTML report, multiple IP addresses via IP aliasing, etc. License: GNU GPLv2.
11. Web Polygraph
Web Polygraph is a workload generator tool that can simulate HTTP, FTP, SSL traffic for benchmarking. It comes with HTTP client and server which, together, can stress test caching proxies, web server accelerators, content filters, etc. Support for LDAP credentials, basic/NTLM/Kerberos authentication is available. License: Apache v2.0.
12. Wrk
wrk is a scalable HTTP benchmarking tool which leverages lightweight event notifications like epoll and kqueue. Support for LuaJIT-scripted workloads, HTTP pipelining, authentication token, dynamic requests, and customizable report is available. License: Apache v2.0.
13. Locust
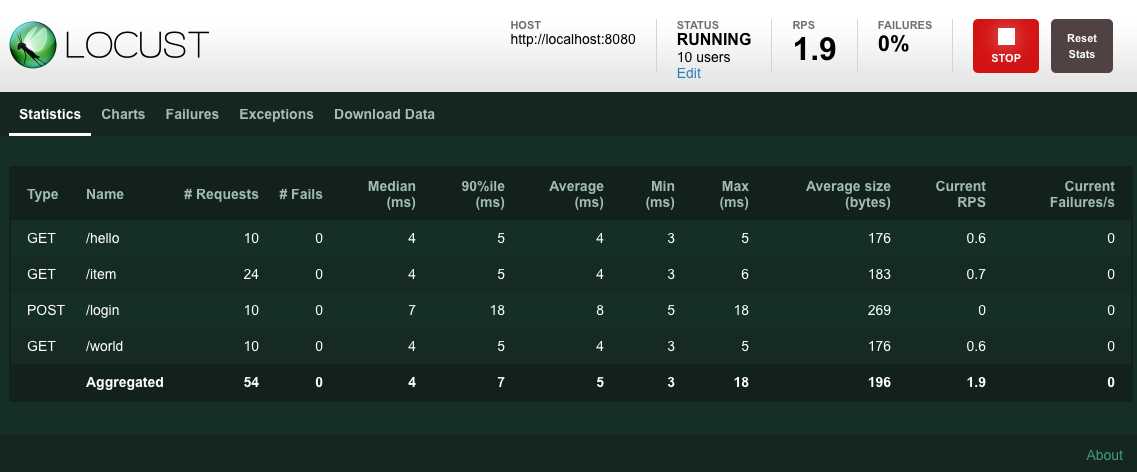
Locust is an open-source load testing tool for web services. You can define user behaviors in your load test in Python code and easily deploy the load test across multiple servers to simulate a large number of concurrent users accessing your web service. Locust provides a web-based interface to monitor various performance statistics (min, max, median, 90-percentile latencies, request rate, sucess/failure ratio, etc). License: MIT.
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

